It won’t come as a surprise when I say cardiovascular diseases is the number one cause for disabilities and/or fatalities globally.
However, you might be surely surprised to know that 80 per cent of heart attacks happen in people with normal cholesterol levels. The increase in young people having heart attacks is dramatically on the rise and more so, over the last 2 decades.
Most people usually go through the routine ‘lipid profile’ test and presume that it is enough to declare themselves ‘heart-healthy’. But there is this new chemical compound in the body that is lately trending globally with its association to heart disease called the Homocysteine. As mouthful as it is to pronounce, it plays a very important role in a process called “methylation” in the body, without which the basic cell functions would be rendered useless.
As per research, homocysteine is 40 times more accurate in predicting heart disease in comparison to cholesterol testing, and so, if you do have a family history of cardiovascular disease, or a known mutation in the MTHFR gene you might want to get it tested annually.
So, what exactly is Homocysteine?
It is a common amino acid (one of the building blocks that make proteins) naturally found in the blood. Homocysteine (Hcy) is naturally produced as a by-product of protein breakdown and is predominantly obtained from meat products in the diet.
Increased levels of homocysteine (Hcy) in the blood resulting in hyperhomocysteinemia (HHcy) have been implicated in cardiac pathological conditions including coronary heart disease (CHD), acute myocardial infarction (MI) and sudden cardiac death (SCD).
Why is high level of Homocysteine considered harmful?
In a healthy person, serum homocysteine levels are around 5 to 15 micromoles per litre (mcmol/L). High levels of homocysteine in the blood called hyperhomocysteinemia (HHcy) can damage the lining of the arteries or cause hardening therein leading to Atherosclerosis. High levels may also make the blood clot more easily than it should. This can increase the risk of blood vessel blockages. A clot (thrombus) can travel in the bloodstream and from there, it can get stuck in your:
- Lungs (called a pulmonary embolism)
- Brain (which can cause a stroke).
- Heart (which can cause a heart attack).
Some people have very high levels of homocysteine and are at an increased risk for heart disease.
And that’s not all! Elevated homocysteine has been associated with other non-heart related issues such as:
- Infertility
- Alopecia areata (spot baldness). Excessive hair fall in only a certain part of your scalp is a major indicator.
- Frequent headaches
- Migraines with aura
- Breathing difficulty
- Vitiligo – white patches that spread throughout the body due to destruction of the skin pigment melanin.
Could I have elevated Homocysteine?
Good question! Elevated levels of homocysteine aren’t so uncommon, and aren’t to be feared. Anyone could be at a risk of elevated homocysteine, as the chances are high either way in the following circumstances;
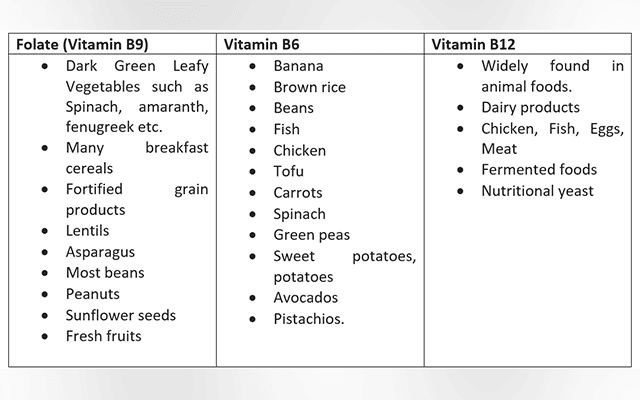
Deficiency of Vitamin B12, folic acid(B9) and Vitamin B6- These are key vitamins that act as catalyst or “middlemen” and help the conversion of homocysteine into other substances that your body needs! Reinstating these vitamins often helps return the homocysteine level to normal.
Mutation in the MTHFR gene- This gene has got a lot of attention in the medical industry lately, and a mutation in this gene is responsible for the build up of homocysteine in the blood. If you have a strong family history of heart disease, a simple genetic test to check for the mutation will help you prevent a heart related complication even 10 years from now!
Other possible causes of elevated homocysteine levels:
- Low levels of thyroid hormone in conditions like Hypothyroidism
- Kidney disease.
- Some medicines.
If you fall into either of the above categories, getting Homocysteine levels evaluated is going to be key in not just preventing heart disease, but also for general health and wellness.
Let us finally answer the golden question!
How do I prevent and/or correct my homocysteine levels?
Here are ways to maintain healthy levels of Homocysteine;
- Dietary intake of Vitamins B12, B6 and Folate
- Supplementation with Methyl folate, Methyl cobalamin, B6, B2 and zinc (if homocysteine levels are elevated)
In my practice as a genetic counsellor and a dietitian I have encountered so many people who are oblivious to even the existence of homocysteine. Do I blame them? Of course not! As people in the health and wellness industry, it is our sole duty to guide and educate people on simple concepts, and a very important as this one, that can eventually save a life.
Talking to your doctor and a qualified dietitian will help you assess your heart health better in which case you may be able to secure a healthy heart for you and your loved ones. Opt for once-in-a-lifetime genetic testing and predict your risk factors well in advance save yourself from expensive medical interventions and experience good health.


















